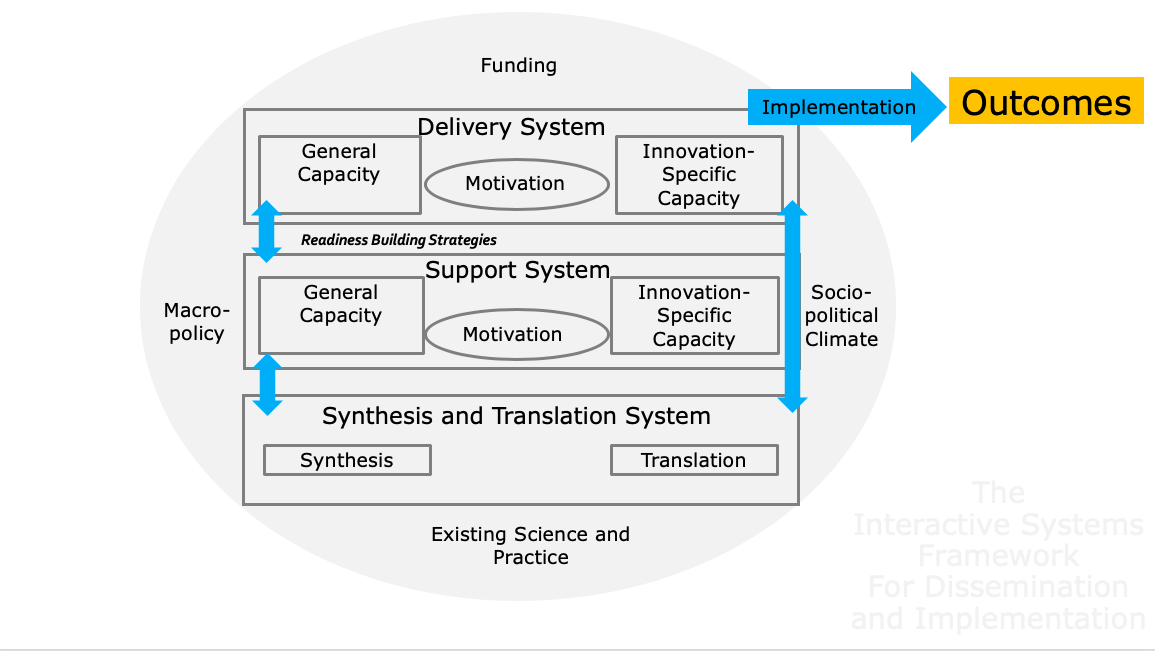
Interactive Systems Framework
D and/or I:
 The focus on dissemination and/or implementation activities. D-only focuses on an active approach of spreading evidence-based interventions to target audience via determined channels using planned strategies. D=I, D>I, and I>D means there is some focus on both dissemination and implementation. I-only focuses on process of putting to use or integrating evidence-based interventions within a setting.
The focus on dissemination and/or implementation activities. D-only focuses on an active approach of spreading evidence-based interventions to target audience via determined channels using planned strategies. D=I, D>I, and I>D means there is some focus on both dissemination and implementation. I-only focuses on process of putting to use or integrating evidence-based interventions within a setting.
D=I Socio-Ecological Levels:
 The level of the framework at which the model operates. Individual includes personal characteristics; Organization includes hospitals, service organizations, and factories; Community includes local government and neighborhoods; System includes hospital systems and government; Policy includes changes in policy.
The level of the framework at which the model operates. Individual includes personal characteristics; Organization includes hospitals, service organizations, and factories; Community includes local government and neighborhoods; System includes hospital systems and government; Policy includes changes in policy.
- Individual
- Organization
- Community
- System
Number of Times Cited:
 The # of times the original publication for the model was cited as indicated by Google Scholar since 2016.
The # of times the original publication for the model was cited as indicated by Google Scholar since 2016.
422 Field of Origin:
 The field of study in which the model originated.
The field of study in which the model originated.
Violence prevention Rating:
 These are ratings given by users of the site.
These are ratings given by users of the site.
Constructs:
 Name of the construct developed by classifying/aligning the elements abstracted from models.
Name of the construct developed by classifying/aligning the elements abstracted from models.
Assessment Instruments:
- AHRQ Digital Health Equity Framework
- CFIR Interview Guide (Lam)
- CFIR Interview Guide (Zhao)
- CFIR Interview Guide Webtool
- Clinical Sustainability Assessment Tool (CSAT)
- Context Matters Reporting Template
- FRAME-IS Adaptation Tracking Instrument
- Glisson's Organizational Social Context (OSC)
- Implementation Climate Scale (ICS)
- Implementation Leadership Scale (ILS)
- Implementation Strategy Usability Scale
- Intervention Scalability Assessment Tool (ISAT)
- Iterative, Practical, Robust Implementation and Sustainability Model (iPRISM) Webtool
- Local Wellness Policy Implementation Checklist
- Normalization Process Theory Interview Guide
- Normalization Process Theory Questionnaire (NoMAD)
- PRISM Contextual Survey Instrument (PCSI)
- PRISM Interview Guide
- Partnership/Synergy Assessment Tool
- Policy Coalition Evaluation Tool (PCET)
- Program Sustainability Assessment Tool (PSAT)
- RAPICE Protocol, Activity, and Interview Prompt Guide
- RAPICE Summary Template
- Readiness Thinking Tool - Observation Guide
- Readiness Thinking Tool - Survey
- Readiness for Recovery and Resiliency - Interview Guide
- Rehabilitation Policy Questionnaire
- Research Engagement Survey Tool (REST)
- Research Engagement Survey Tool (REST) - 9 item
- Short Program Sustainability Assessment Tool (PSAT)
- Stages of Implementation Completion (SIC)
- Van Schaik's Technology Acceptance Model (TAM)
- i-PARiHS Interview Guide
Citations:
 The original publication(s) of the model.
The original publication(s) of the model.
Wandersman A, Duffy J, Flaspohler P, et al. Bridging the gap between prevention research and practice: the interactive systems framework for dissemination and implementation. Am J Community Psychol 2008;41(3-4):171–81. Examples:
 Citations of studies that have used the model as an outline for their study.
Citations of studies that have used the model as an outline for their study.
Belone L, Rae R, Hirchak KA, Cohoe-Belone B, Orosco A, Shendo K, Wallerstein N. Dissemination of an American Indian Culturally Centered Community-Based Participatory Research Family Listening Program: Implications for Global Indigenous Well-Being. Genealogy. 2020; 4(4):99. doi.org/10.3390/genealogy4040099Emshoff JG. Researchers, practitioners, and funders: using the framework to get us on the same page. Am J Commun Psychol 2008;41(3):393-403.
Firesheets EK, Francis M, Barnum A, Rolf L. Community-based prevention support: using the interactive systems framework to facilitate grassroots evidenced-based substance abuse prevention. Am J Community Psychol. 2012 Dec;50(3-4):347-56. doi: 10.1007/s10464-012-9506-x.
Florin P, Friend KB, Buka S, Egan C, Barovier L, Amodei B. The interactive systems framework applied to the strategic prevention framework: the Rhode Island experience. Am J Community Psychol. 2012 Dec;50(3-4):402-14. doi: 10.1007/s10464-012-9527-5.
Hirchak KA, Hernandez-Vallant A, Herron J, Cloud V, Tonigan JS, McCrady B, Venner K. Aligning three substance use disorder interventions among a tribe in the Southwest United States: Pilot feasibility for cultural re-centering, dissemination, and implementation. J Ethn Subst Abuse. 2020 Nov 2:1-17. doi: 10.1080/15332640.2020.1836701.
Lee SJ, Altschul I, Mowbray CT. Using planned adaptation to implement evidence-based programs with new populations. Am J Community Psychol. 2008 Jun;41(3-4):290-303. doi: 10.1007/s10464-008-9160-5.
Lesesne CA, Lewis KM, White CP, Green DC, Duffy JL, Wandersman A. Promoting science-based approaches to teen pregnancy prevention: proactively engaging the three systems of the interactive systems framework. Am J Community Psychol. 2008 Jun;41(3-4):379-92. doi: 10.1007/s10464-008-9175-y.
Ozer EJ, Cantor JP, Cruz GW, Fox B, Hubbard E, Moret L. The diffusion of youth-led participatory research in urban schools: the role of the prevention support system in implementation and sustainability. Am J Community Psychol. 2008 Jun;41(3-4):278-89. doi: 10.1007/s10464-008-9173-0.
Rolleri LA, Wilson MM, Paluzzi PA, Sedivy VJ. Building capacity of state adolescent pregnancy prevention coalitions to implement science-based approaches. Am J Community Psychol. 2008 Jun;41(3-4):225-34. doi: 10.1007/s10464-008-9177-9.
Sprague Martinez L, Dimitri N, Ron S, Hudda N, Zamore W, Lowe L, Echevarria B, Durant JL, Brugge D, Reisner E. Two communities, one highway and the fight for clean air: the role of political history in shaping community engagement and environmental health research translation. BMC Public Health. 2020 Nov 11;20(1):1690. doi: 10.1186/s12889-020-09751-w.
Taylor LK, Weist MD, DeLoach K. Exploring the use of the interactive systems framework to guide school mental health services in post-disaster contexts: building community capacity for trauma-focused interventions. Am J Community Psychol. 2012 Dec;50(3-4):530-40. doi: 10.1007/s10464-012-9501-2.
There are no reviews yet. Be the first one to write one.