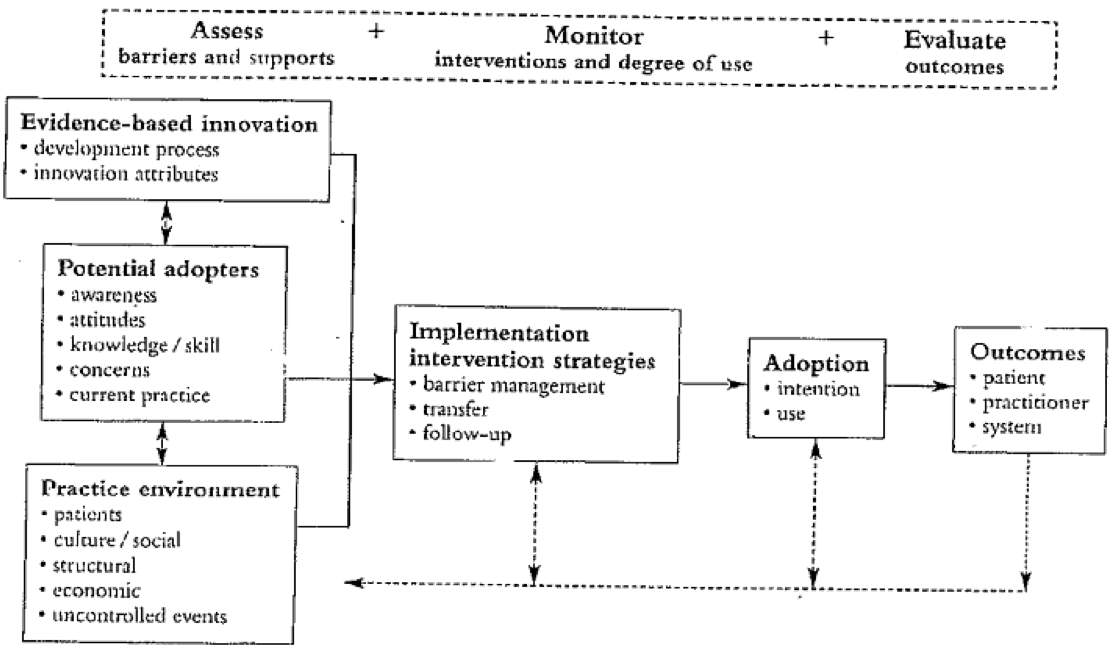
Ottawa Model of Research Use
D and/or I:
 The focus on dissemination and/or implementation activities. D-only focuses on an active approach of spreading evidence-based interventions to target audience via determined channels using planned strategies. D=I, D>I, and I>D means there is some focus on both dissemination and implementation. I-only focuses on process of putting to use or integrating evidence-based interventions within a setting.
The focus on dissemination and/or implementation activities. D-only focuses on an active approach of spreading evidence-based interventions to target audience via determined channels using planned strategies. D=I, D>I, and I>D means there is some focus on both dissemination and implementation. I-only focuses on process of putting to use or integrating evidence-based interventions within a setting.
D=I Socio-Ecological Levels:
 The level of the framework at which the model operates. Individual includes personal characteristics; Organization includes hospitals, service organizations, and factories; Community includes local government and neighborhoods; System includes hospital systems and government; Policy includes changes in policy.
The level of the framework at which the model operates. Individual includes personal characteristics; Organization includes hospitals, service organizations, and factories; Community includes local government and neighborhoods; System includes hospital systems and government; Policy includes changes in policy.
- Individual
- Organization
- Community
Number of Times Cited:
 The # of times the original publication for the model was cited as indicated by Google Scholar since 2016.
The # of times the original publication for the model was cited as indicated by Google Scholar since 2016.
82 Field of Origin:
 The field of study in which the model originated.
The field of study in which the model originated.
Health care Rating:
 These are ratings given by users of the site.
These are ratings given by users of the site.
Constructs:
 Name of the construct developed by classifying/aligning the elements abstracted from models.
Name of the construct developed by classifying/aligning the elements abstracted from models.
Assessment Instruments:
- CFIR Interview Guide (Lam)
- CFIR Interview Guide (Zhao)
- CFIR Interview Guide Webtool
- Clinical Sustainability Assessment Tool (CSAT)
- Implementation Leadership Scale (ILS)
- Iterative, Practical, Robust Implementation and Sustainability Model (iPRISM) Webtool
- Local Wellness Policy Implementation Checklist
- Normalization Process Theory Interview Guide
- PRISM Interview Guide
- Partnership/Synergy Assessment Tool
- Policy Coalition Evaluation Tool (PCET)
- RAPICE Protocol, Activity, and Interview Prompt Guide
- RAPICE Summary Template
- Research Engagement Survey Tool (REST)
- Research Engagement Survey Tool (REST) - 9 item
- Stages of Implementation Completion (SIC)
Citations:
 The original publication(s) of the model.
The original publication(s) of the model.
Logan J, Graham ID. Toward a comprehensive interdisciplinary model of health care research use. Sci Commun 1998;20(2):227.
Logan J, Graham ID. The Ottawa Model of Research Use. In: Bucknall JR-MaT, ed. Models and frameworks for implementating evidence-based practice: evidence to action. Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell, 2010. Examples:
 Citations of studies that have used the model as an outline for their study.
Citations of studies that have used the model as an outline for their study.
Campbell B. Applying knowledge to generate action: a community-based knowledge translation framework. J Contin Educ Health Prof 2010;30(1):65-71.Driedger SM, Kothari A, Graham ID, et al. If you build it, they still may not come: outcomes and process of implementing a community-based integrated knowledge translation mapping innovation. Implemen Sci 2010;5.
Gifford WA, Davies B, Graham ID, Lefebre N, Tourangeau A, Woodend K. A mixed methods pilot study with a cluster randomized control trial to evaluate the impact of a leadership intervention on guideline implementation in home care nursing. Implem Sci 2008;3:51.
Graham K, Logan J. Using the Ottawa model of research use to implement a skin care program. J Nurs Care Qual 2004;19(1):18-24.
Hogan DL, Logan JO. The Ottawa model of research use: a guide to clinical innovation in the NICU. Clin Nurse Spec 2004;18(5):255.
Kothari A, Driedger SM, Bickford J, et al. Mapping as a knowledge translation tool for Ontario Early Years Centres: views from data analysts and managers. Implemen Sci 2008;3.
There are no reviews yet. Be the first one to write one.