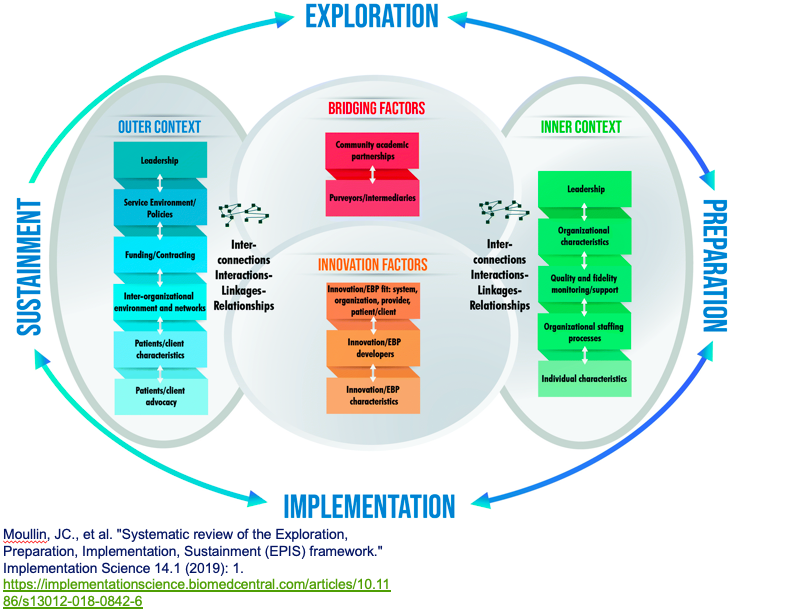
Exploration, Preparation, Implementation, Sustainment (EPIS) model (Conceptual Model of Evidence-based Practice Implementation in Public Service Sectors)
D and/or I:
 The focus on dissemination and/or implementation activities. D-only focuses on an active approach of spreading evidence-based interventions to target audience via determined channels using planned strategies. D=I, D>I, and I>D means there is some focus on both dissemination and implementation. I-only focuses on process of putting to use or integrating evidence-based interventions within a setting.
The focus on dissemination and/or implementation activities. D-only focuses on an active approach of spreading evidence-based interventions to target audience via determined channels using planned strategies. D=I, D>I, and I>D means there is some focus on both dissemination and implementation. I-only focuses on process of putting to use or integrating evidence-based interventions within a setting.
I-Only Socio-Ecological Levels:
 The level of the framework at which the model operates. Individual includes personal characteristics; Organization includes hospitals, service organizations, and factories; Community includes local government and neighborhoods; System includes hospital systems and government; Policy includes changes in policy.
The level of the framework at which the model operates. Individual includes personal characteristics; Organization includes hospitals, service organizations, and factories; Community includes local government and neighborhoods; System includes hospital systems and government; Policy includes changes in policy.
- Individual
- Organization
- Community
- System
- Policy
Number of Times Cited:
 The # of times the original publication for the model was cited as indicated by Google Scholar since 2016.
The # of times the original publication for the model was cited as indicated by Google Scholar since 2016.
898 Field of Origin:
 The field of study in which the model originated.
The field of study in which the model originated.
Public sector services Practitioner/Researcher:
 Whether the model is for the use of practitioners and/or researchers.
Whether the model is for the use of practitioners and/or researchers.
Researcher Rating:
 These are ratings given by users of the site.
These are ratings given by users of the site.
Constructs:
 Name of the construct developed by classifying/aligning the elements abstracted from models.
Name of the construct developed by classifying/aligning the elements abstracted from models.
- Acceptability/feasibility
- Adopter/implementer/decision maker characteristics
- Adoption
- Awareness
- Development of an Intervention
- Barriers and facilitators
- Champion/field agent
- Communication channels
- Fidelity
- Fit
- Implementation
- Knowledge and Knowledge Synthesis
- Pre-implementation
- Maintenance, Sustainability and Scale-up
- Stakeholders
- Strategies
Assessment Instruments:
- AHRQ Digital Health Equity Framework
- Acceptability of Intervention Measure (AIM)
- CFIR Interview Guide (Lam)
- CFIR Interview Guide (Zhao)
- CFIR Interview Guide Webtool
- Clinical Sustainability Assessment Tool (CSAT)
- Diagnosis Related Group (DRG) Policy Survey
- Evidence Based Practice Attitude Scale (EBPAS)
- FRAME-IS Adaptation Tracking Instrument
- Feasibility of Intervention Measure (FIM)
- Goodman's Level of Institutionalization
- Hall's Levels of Use Scale
- Implementation Climate Scale (ICS)
- Implementation Leadership Scale (ILS)
- Implementation Strategy Usability Scale
- Intervention Appropriateness Measure (IAM)
- Intervention Scalability Assessment Tool (ISAT)
- Iterative, Practical, Robust Implementation and Sustainability Model (iPRISM) Webtool
- Landry's Knowledge Utilization Scale among Policymakers
- Local Wellness Policy Implementation Checklist
- Local Wellness Policy Survey
- Normalization Process Theory Interview Guide
- Normalization Process Theory Questionnaire (NoMAD)
- Organizational Readiness for Implementing Change (ORIC)
- PRISM Contextual Survey Instrument (PCSI)
- PRISM Interview Guide
- Partnership/Synergy Assessment Tool
- Policy Coalition Evaluation Tool (PCET)
- Program Sustainability Index
- RAPICE Protocol, Activity, and Interview Prompt Guide
- RAPICE Summary Template
- Readiness Thinking Tool - Observation Guide
- Readiness Thinking Tool - Survey
- Readiness for Recovery and Resiliency - Interview Guide
- Rehabilitation Policy Questionnaire
- Research Engagement Survey Tool (REST)
- Research Engagement Survey Tool (REST) - 9 item
- Stages of Implementation Completion (SIC)
- Van Schaik's Technology Acceptance Model (TAM)
- i-PARiHS Interview Guide
Website:
 Website.
Website.
https://episframework.com/
Citations:
 The original publication(s) of the model.
The original publication(s) of the model.
Aarons GA, Hurlburt M, Horwitz SM. Advancing a conceptual model of evidence-based practice implementation in public service sectors. Admin Policy Mental Health 2011;38(1):4–23.
Moullin JC, Dickson KS, Stadnick NA, Rabin B, Aarons GA. Systematic review of the Exploration, Preparation, Implementation, Sustainment (EPIS) framework. Implement Sci. 2019 Jan 5;14(1):1. Examples:
 Citations of studies that have used the model as an outline for their study.
Citations of studies that have used the model as an outline for their study.
Aarons GA, Fettes DL, Sommerfeld DH, Palinkas LA: Mixed methods for implementation research: Application to evidence-based practice implementation and staff turnover in community-based organizations providing child welfare services. Child Maltreatment 2012, 17:67-79.Aarons GA, Green AE, Trott E, Willging C, Torres EM, Ehrhart M, Roesch SC. The roles of system and organizational leadership in system-wide evidence-based intervention sustainment: A mixed-method study. Adm Policy Ment Hlth 2016, 43:991-1008.
Brookman-Frazee L, Chlebowski C, Suhrheinrich J, et al. Characterizing Shared and Unique Implementation Influences in Two Community Services Systems for Autism: Applying the EPIS Framework to Two Large-Scale Autism Intervention Community Effectiveness Trials. Adm Policy Ment Health. 2020;47(2):176-187. doi:10.1007/s10488-019-00931-4
Idalski Carcone A, Coyle K, Gurung S, et al. Implementation Science Research Examining the Integration of Evidence-Based Practices Into HIV Prevention and Clinical Care: Protocol for a Mixed-Methods Study Using the Exploration, Preparation, Implementation, and Sustainment (EPIS) Model. JMIR Res Protoc. 2019;8(5):e11202. Published 2019 May 23. doi:10.2196/11202
Stadnick NA, Meza RD, Suhrheinrich J, et al. Leadership profiles associated with the implementation of behavioral health evidence-based practices for autism spectrum disorder in schools. Autism. 2019;23(8):1957-1968. doi:10.1177/1362361319834398
There are no reviews yet. Be the first one to write one.